- Andy Chia-Hao Chang/
- Projects/
- People Say AI: Natural Language Querying for Qualitative Research Data/
People Say AI: Natural Language Querying for Qualitative Research Data
Table of Contents
People Say AI: Leveraging AI for Qualitative Research Analysis
People Say AI is a collaborative project with the Public Policy Lab (PPL) that explores the potential of artificial intelligence to democratize access to qualitative research data. Built to query The People Say database—a comprehensive collection of older adults’ experiences in the United States funded by The SCAN Foundation—the application demonstrates how large language models can enhance rather than replace human research capabilities.
Project Overview #
Public Policy Lab’s mission is to optimize government services by conducting qualitative research to uncover nuanced “thick data.” As PPL researchers often say, they are “looking for divergence, not the mean” to understand how policies affect individuals differently.
However, a significant bottleneck exists in their workflow: while clustering and tagging data is relatively fast, synthesizing insights from 2,400+ data units (derived from over 100 hours of interviews) is time- and resource-intensive. This project investigates how we can leverage AI to assist in this synthesis bottleneck, helping researchers explore complex qualitative datasets more efficiently while preserving the critical outliers and depth that make qualitative research valuable.
The application provides an intuitive interface where users can ask questions in plain English, which are then translated into data-driven insights. By bridging the gap between natural language and structured data, People Say AI makes valuable community perspectives more accessible to researchers, policymakers, and advocates. As noted by The People Say, the platform features older adults talking about their lives and the policy issues that affect them, including housing, healthcare, and financial security.
Key Capabilities #
Natural Language to SQL Querying #
Traditional data retrieval often requires specialized knowledge of SQL or database schemas. People Say AI simplifies this by using prompt engineering to convert natural language questions into precise SQL queries. This allows users to focus on their research questions rather than the technicalities of data retrieval. The system remains transparent by displaying the generated SQL, allowing for verification and trust.
AI-Powered Analysis & Summarization #
Once relevant data excerpts are retrieved, the application leverages Gemini models to synthesize the findings. Users can choose from different analytical frameworks—such as Thematic Analysis, Narrative Analysis, or Comparative Analysis—to guide how the model interprets the data. This flexibility ensures that the insights generated align with specific research methodologies.
Integrity through Source Citation #
A critical challenge in using AI for research is ensuring accuracy and preventing hallucinations. People Say AI addresses this by implementing an automatic citation system. Every summary generated includes direct references and quotes from the specific database excerpts used, ensuring full traceability from the AI’s answer back to the original human experience.
Technical Implementation #
The application is built with a modular architecture focused on transparency and research integrity:
- Frontend: Developed using Streamlit to provide a responsive, researcher-focused interface for real-time data exploration.
- Orchestration: A core logic engine manages the pipeline, coordinating between LLM inference (Gemini API), SQLite database operations, and result formatting.
- Prompt Engineering: Carefully crafted prompts ensure that the AI generates valid SQL and produces summaries that maintain the nuance of the original qualitative data.
My Role & Contributions #
As the lead developer within our team (which included members focused on Operations Research and Law), I worked closely with the Public Policy Lab to translate research needs into a functional AI application. My contributions included:
- System Architecture: Designing and building the full-stack application, from the SQLite database schema to the Streamlit frontend.
- AI Methodology: Developing and testing prompt strategies that ensure high-fidelity data retrieval and context-aware summarization.
- Research Integrity: Implementing the source citation system to ensure that every AI-generated insight is grounded in the original dataset, directly addressing LLM hallucination risks.
- User Experience: Designing a workflow that makes complex AI processes transparent and approachable for non-technical researchers.
Impact & Success Indicators #
The tool is designed to modernize the research workflow, helping PPL and its government partners work faster and more efficiently. Success for this project is measured by:
- Intuitive Adoption: Researchers find the tool easy to integrate into their existing thematic coding and sentiment analysis workflows.
- Discovery of Outliers: The ability to quickly locate specific, nuanced quotes that represent critical “divergent” experiences rather than just high-level trends.
- Scalability: The infrastructure allows for new data units to be added seamlessly, increasing the pool of insights available for policy proposals.
Features and Screenshots #
Intuitive Search Interface #
The homepage provides a clean interface where users can enter natural language queries and configure API settings.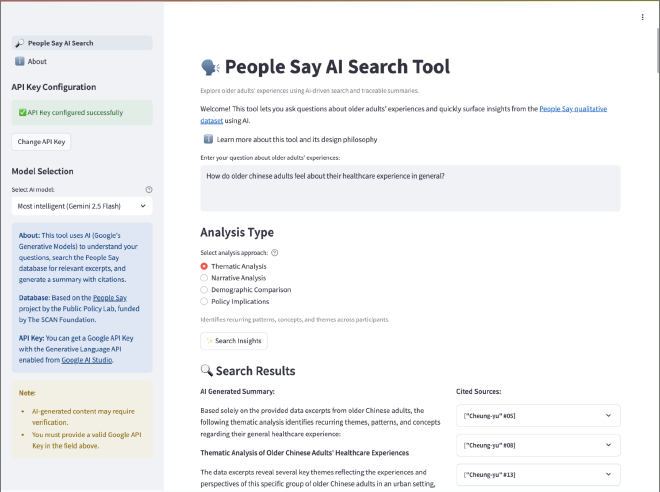
Analysis Tool #
Researchers can explore AI-driven analysis through multiple crafted prompts.
Summarization with Source Citations #
The tool generates comprehensive summaries that are directly linked to the underlying qualitative data, ensuring transparency and preventing hallucination.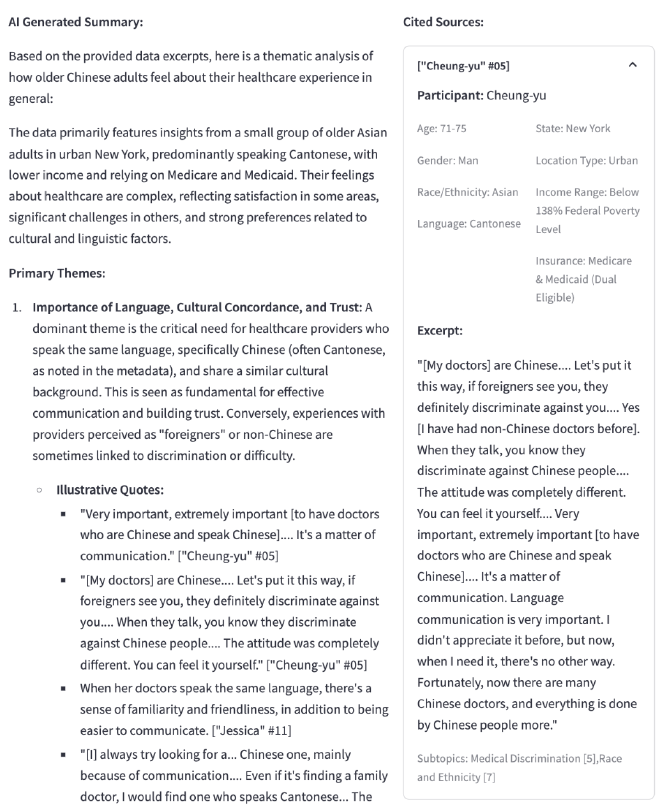
Conclusion #
This collaboration highlights the potential for AI to serve as a powerful “co-pilot” for researchers. By making complex qualitative datasets more searchable and summarizable, it makes the research process smoother and approachable. It stands as a model for how large language models can be deployed responsibly in research contexts—augmenting human insight while maintaining strict standards for transparency and attribution.